Dimensional coordination
Important technical terms and dimensions for ref-erence
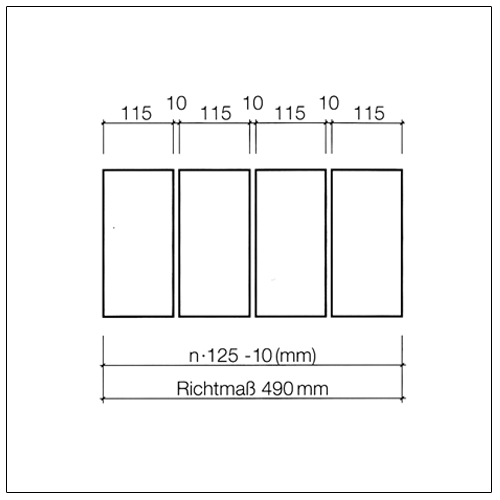
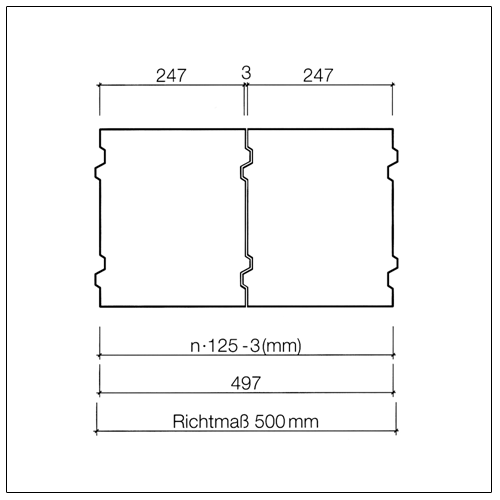
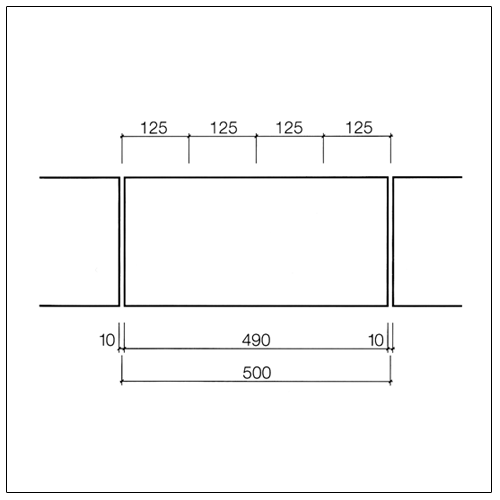
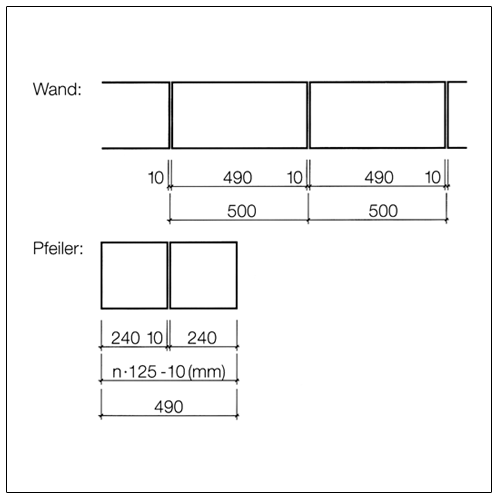
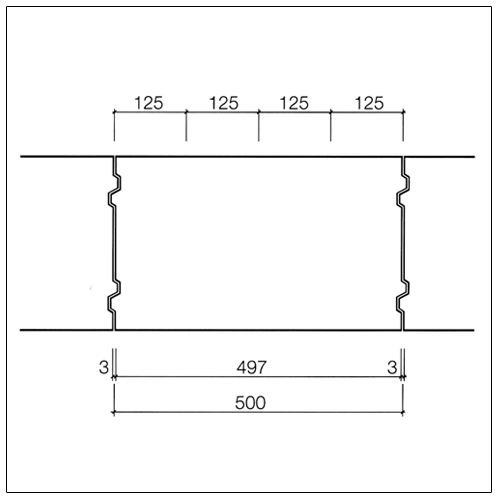
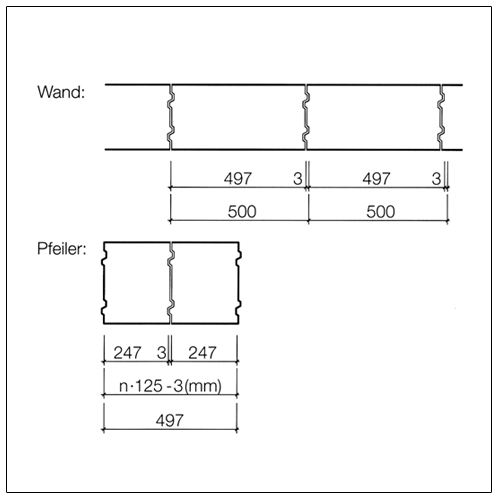
Dimensional coordination in structural engineering according to DIN 4172 is based on the dimension 12.5 cm (octometric dimension based on 1/8 metre = 0.125 m). The basic dimensions are (except for a few design exceptions) therefore even multiples of 12.5 cm.
The dimension terms are:
- Basic dimensions: Dimensions of components including their joints
- Nominal dimensions: Dimensions that the components should have
- Maximum dimension: maximum permitted dimension
- Minimum dimension: minimum permitted dimension
- Dimensional tolerance: Difference between maximum dimension and minimum dimension
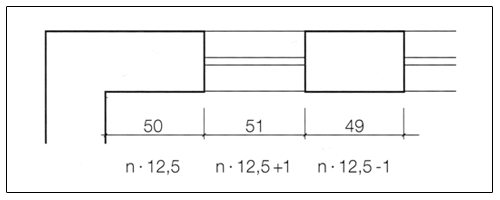
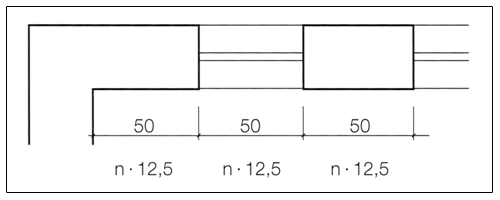
For the dimensioning of masonry the following approaches apply.
|
Basic dimensions |
Nominal size |
|
|---|---|---|
|
Exterior dimension |
n × 12,5 cm |
n × 12,5 cm – 1 cm |
|
Opening dimension |
n × 12,5 cm |
n × 12,5 cm + 1 cm |
|
Lead dimension |
n × 12,5 cm |
n × 12,5 cm |
For the block heights the octametric system also applies, even though today a layer dimension of 25 cm (4 layers one metre) is used. Blocks with other heights result in this dimension including the horizontal joint mortar. For components without mortared joints the nominal dimensions are equal to the basic dimensions. For KLB flat block masonry the block heights are adjusted.