Tolerances for masonry construction
Dimensions and tolerances for building with KLB masonry in overview
The following tabs are meant to provide a brief overview of the different tolerances and dimensions, which must be adhered to when building with KLB masonry.
- Dimension
- Joint thickness
- Limit dimension
- Angle tolerance
- Levelness tolerance
Dimensions
The permitted tolerances for masonry are specified in DIN 18 202. The permitted tolerances for the dimensions of the KLB blocks are specified in the main block standards, DIN V 18151-100, DIN V 18152-100, DIN V 18153-100 or in the approvals of KLB. They are:
|
Type of block |
permitted tolerance in mm |
||
|
|
Length |
Width |
Height |
|
KLB-Kalopor |
± 3 |
± 3 |
± 1,0 |
|
KLB flat blocks |
± 3 |
± 3 |
± 1,0 |
|
KLB flat solid blocks |
± 3 |
± 3 |
± 1,0 |
|
KLBQUADRO |
± 3 |
± 3 |
± 1,0 |
|
KLB blocks |
± 3 |
± 3 |
± 4 |
|
KLB solid blocks |
± 3 |
± 3 |
± 3 |
Deviations in the block dimensions are statistically distributed. This means that e.g. for several blocks lying behind one another in one layer the target dimension is nearly maintained as shorter and longer blocks are equally often represented.
Joint thickness
For masonry with non-mortared butt joints the blocks must be bumped tightly according to DIN 1053 Part 1, where the opening width of the butt joint must not exceed the dimension of 5 mm. At KLB the designed opening width of the butt joint is ≤ 3 mm. During the blunt bump at the construction site the opening width of the butt joint moves to 0 mm.
The horizontal joints are supposed to be 12 mm thick when using light-weight or normal mortar. For small-format masonry with mortared butt joints the thickness of the butt joints is supposed to be 10 mm. Permitted deviations for these joint thicknesses to be maintained as an average are not listed. However, it should be noted that deviations in the joint thickness makes maintaining the layer dimensions more difficult and can lead to problems for wall integrations.
For thin-bed mortar the joint thickness of the horizontal joint and butt joint, here for blocks without tongue and groove connection, should be at least 1 mm and at most 3 mm. KLB supplementary products such as offset blocks, ceiling wall blocks, U blocks or falls must always be mortared with thick-bed joints.
Limit dimension
|
Nominal size in m |
Maximum permitted deviation from the nominal size in mm |
|||
|
|
L1 |
L2 |
L3 |
L4 |
|
≤ 3 |
± 12 |
± 16 |
± 20 |
± 12 |
|
> 3 ≤ 6 |
± 16 |
± 16 |
± 20 |
± 16 |
|
> 6 ≤ 15 |
± 20 |
± 20 |
± 30 |
- |
|
> 15 ≤ 30 |
± 24 |
± 30 |
- |
- |
|
> 30 |
± 30 |
± 30 |
- |
- |
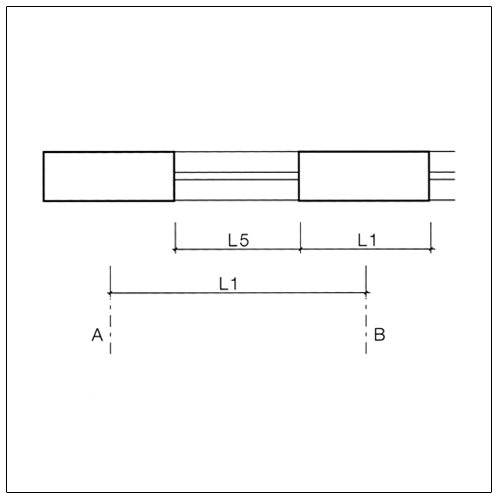
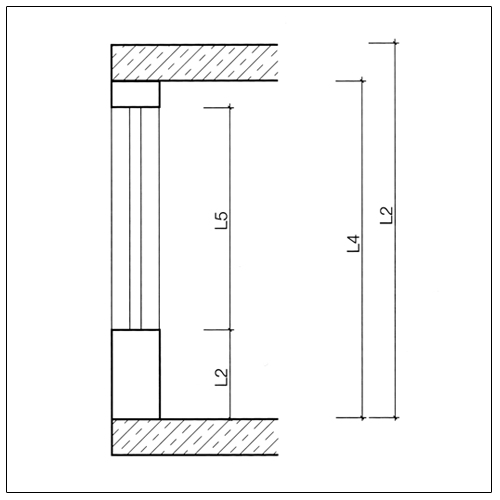
L1: Dimensions in the floor plan, e.g. wall lengths, axis and grid dimensions
L2: Dimensions in the cross section, e.g. storey heights
L3: Clear dimensions in the cross section, e.g. clear storey height
L4: Openings, e.g. doors and windows
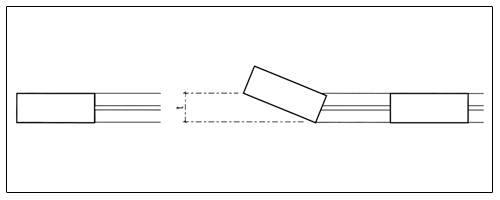
Flatness tolerances for walls in the shell construction state
|
Nominal dimensions in m |
Precision dimension t in mm |
|
< 1 |
≤ 6 |
|
≥ 1 ≤ 3 |
≤ 8 |
|
≥ 3 ≤ 6 |
≤ 12 |
|
≥ 6 ≤ 15 |
≤ 16 |
|
≥ 15 ≤ 30 |
≤ 20 |
|
> 30 |
≤ 30 |
Flatness tolerances for walls in the shell construction state
|
Distance of the measurement points e in mm |
Precision dimension s in mm |
|
0,1 |
≤ 5 |
|
1,0 |
≤ 10 |
|
4,0 |
≤ 15 |
|
10,0 |
≤ 25 |
|
15,0 |
≤ 30 |
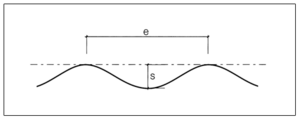
Interim values of flatness tolerances must be interpolated in a straight line and rounded to whole millimetres. If the block width equals the wall width, the flatness tolerances only apply to the flush side. For the non-flush side the tolerances according to DIN 18202 plus the tolerances of the blocks apply.

